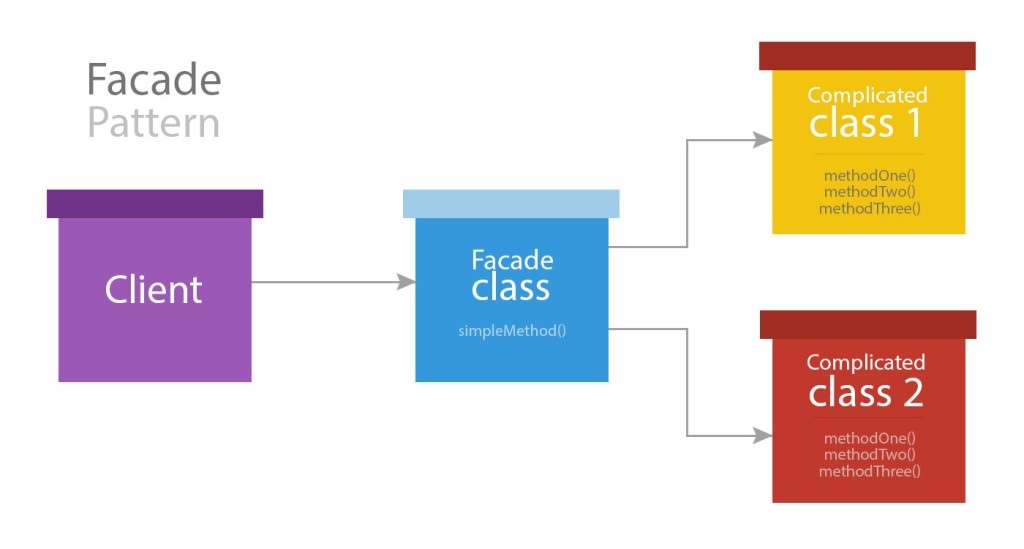
简介
注:对门面这个概念不理解?可参考PHP 设计模式系列 —— 门面模式(Facade)。
门面为应用服务容器中的绑定类提供了一个“静态”接口。Laravel 内置了很多门面,你可能在不知道的情况下正在使用它们。Laravel 的门面作为服务容器中底层类的“静态代理”,相比于传统静态方法,在维护时能够提供更加易于测试、更加灵活、简明优雅的语法。
Laravel 的所有门面都定义在 Illuminate\Support\Facades 命名空间下,所以我们可以轻松访问到门面:
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Cache;
Route::get('/cache', function () {
return Cache::get('key');
});
在整个 Laravel 文档中,很多例子使用了门面来演示框架的各种功能特性。
何时使用门面
门面有诸多优点,其提供了简单、易记的语法,让我们无需记住长长的类名即可使用 Laravel 提供的功能特性,此外,由于他们对 PHP 动态方法的独到用法,使得它们很容易测试。
但是,使用门面也有需要注意的地方,一个最主要的危险就是类范围蠕变。由于门面如此好用并且不需要注入,在单个类中使用过多门面,会让类很容易变得越来越大。使用依赖注入则会让此类问题缓解,因为一个巨大的构造函数会让我们很容易判断出类在变大。因此,使用门面的时候要尤其注意类的大小,以便控制其有限职责。
注:构建与 Laravel 交互的第三方扩展包时,最好注入 Laravel 契约而不是使用门面,因为扩展包在 Laravel 之外构建,你将不能访问 Laravel 的门面测试辅助函数。
门面 vs. 依赖注入
依赖注入的最大优点是可以替换注入类的实现,这在测试时很有用,因为你可以注入一个模拟或存根并且在存根上断言不同的方法。
但是在静态类方法上进行模拟或存根却行不通,不过,由于门面使用了动态方法对服务容器中解析出来的对象方法调用进行了代理,我们也可以像测试注入类实例那样测试门面。例如,给定以下路由:
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Cache;
Route::get('/cache', function () {
return Cache::get('key');
});
我们可以这样编写测试来验证 Cache::get 方法以我们期望的方式被调用:
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Cache;
/**
* A basic functional test example.
*
* @return void
*/
public function testBasicExample()
{
Cache::shouldReceive('get')
->with('key')
->andReturn('value');
$this->visit('/cache')
->see('value');
}
门面 vs 辅助函数
除了门面之外,Laravel 还内置了许多辅助函数用于执行通用任务,比如生成视图、触发事件、分配任务,以及发送 HTTP 响应等。很多辅助函数提供了和相应门面一样的功能,例如,下面这个门面调用和辅助函数调用是等价的:
return View::make('profile');
return view('profile');
门面和辅助函数之间并不存在实质性差别,使用辅助函数的时候,可以像测试相应门面那样测试它们。例如,给定以下路由:
Route::get('/cache', function () {
return cache('key');
});
在调用底层, cache 方法会去调用 Cache 门面上的 get 方法,因此,尽管我们使用这个辅助函数,我们还是可以编写如下测试来验证这个方法以我们期望的方式和参数被调用:
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Cache;
/**
* A basic functional test example.
*
* @return void
*/
public function testBasicExample()
{
Cache::shouldReceive('get')
->with('key')
->andReturn('value');
$this->visit('/cache')
->see('value');
}
门面工作原理
在 Laravel 应用中,门面就是一个为容器中对象提供访问方式的类。该机制原理由 Facade 类实现。Laravel 自带的门面,以及我们创建的自定义门面,都会继承自 Illuminate\Support\Facades\Facade 基类。
门面类只需要实现一个方法:getFacadeAccessor。正是 getFacadeAccessor 方法定义了从容器中解析什么,然后 Facade 基类使用魔术方法 __callStatic() 从你的门面中调用解析对象。
下面的例子中,我们将会调用 Laravel 的缓存系统,浏览代码后,也许你会觉得我们调用了 Cache 的静态方法 get:
<?php
namespace App\Http\Controllers;
use Cache;
use App\Http\Controllers\Controller;
class UserController extends Controller{
/**
* 为指定用户显示属性
*
* @param int $id
* @return Response
*/
public function showProfile($id)
{
$user = Cache::get('user:'.$id);
return view('profile', ['user' => $user]);
}
}
注意我们在顶部位置引入了 Cache 门面。该门面作为代理访问底层 Illuminate\Contracts\Cache\Factory 接口的实现。我们对门面的所有调用都会被传递给 Laravel 缓存服务的底层实例。
如果我们查看 Illuminate\Support\Facades\Cache 类的源码,将会发现其中并没有静态方法 get:
class Cache extends Facade
{
/**
* 获取组件注册名称
*
* @return string
*/
protected static function getFacadeAccessor() {
return 'cache';
}
}
Cache 门面继承 Facade 基类并定义了 getFacadeAccessor 方法,该方法的工作就是返回服务容器绑定类的别名,当用户引用 Cache 类的任何静态方法时,Laravel 从服务容器中解析 cache 绑定,然后在解析出的对象上调用所有请求方法(本例中是 get)。
实时门面
使用实时门面,可以将应用中的任意类当做门面来使用。为了说明如何使用这个功能,我们先看一个替代方案。例如我们假设 Podcast 模型有一个 publish 方法,尽管如此,为了发布博客,我们需要注入 Publisher 实例:
<?php
namespace App;
use App\Contracts\Publisher;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Model;
class Podcast extends Model
{
/**
* Publish the podcast.
*
* @param Publisher $publisher
* @return void
*/
public function publish(Publisher $publisher)
{
$this->update(['publishing' => now()]);
$publisher->publish($this);
}
}
因为可以模拟注入的发布服务,所以注入发布实现到该方法后允许我们轻松在隔离状态下测试该方法。不过,这要求我们每次调用 publish 方法都要传递一个发布服务实例,使用实时门面,我们可以在维持这种易于测试的前提下不必显式传递 Publisher 实例。要生成一个实时门面,在导入类前面加上 Facades 命名空间前缀即可:
<?php
namespace App;
use Facades\App\Contracts\Publisher;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Model;
class Podcast extends Model
{
/**
* Publish the podcast.
*
* @return void
*/
public function publish()
{
$this->update(['publishing' => now()]);
Publisher::publish($this);
}
}
使用实时门面后,发布服务实现将会通过使用 Facades 前缀后的接口或类名在服务容器中解析。在测试的时候,我们可以使用 Laravel 自带的门面测试辅助函数来模拟这个方法调用:
<?php
namespace Tests\Feature;
use App\Podcast;
use Tests\TestCase;
use Facades\App\Contracts\Publisher;
use Illuminate\Foundation\Testing\RefreshDatabase;
class PodcastTest extends TestCase
{
use RefreshDatabase;
/**
* A test example.
*
* @return void
*/
public function test_podcast_can_be_published()
{
$podcast = factory(Podcast::class)->create();
Publisher::shouldReceive('publish')->once()->with($podcast);
$podcast->publish();
}
}
门面类列表
下面列出了每个门面及其对应的底层类,这对深入给定根门面的 API 文档而言是个很有用的工具。服务容器绑定键也被包含进来:
| 门面 | 类 | 服务容器绑定 |
|---|---|---|
| App | Illuminate\Foundation\Application | app |
| Artisan | Illuminate\Contracts\Console\Kernel | artisan |
| Auth | Illuminate\Auth\AuthManager | auth |
| Auth(实例) | Illuminate\Contracts\Auth\Guard | auth.driver |
| Blade | Illuminate\View\Compilers\BladeCompiler | blade.compiler |
| Broadcast | Illuminate\Contracts\Broadcasting\Factory | |
| Broadcast(实例) | Illuminate\Contracts\Broadcasting\Broadcaster | |
| Bus | Illuminate\Contracts\Bus\Dispatcher | |
| Cache | Illuminate\Cache\CacheManager | cache |
| Cache(实例) | Illuminate\Cache\Repository | cache.store |
| Config | Illuminate\Config\Repository | config |
| Cookie | Illuminate\Cookie\CookieJar | cookie |
| Crypt | Illuminate\Encryption\Encrypter | encrypter |
| DB | Illuminate\Database\DatabaseManager | db |
| DB(实例) | Illuminate\Database\Connection | db.connection |
| Event | Illuminate\Events\Dispatcher | events |
| File | Illuminate\Filesystem\Filesystem | files |
| Gate | Illuminate\Contracts\Auth\Access\Gate | |
| Hash | Illuminate\Contracts\Hashing\Hasher | hash |
| Lang | Illuminate\Translation\Translator | translator |
| Log | Illuminate\Log\Writer | log |
| Illuminate\Mail\Mailer | mailer | |
| Notification | Illuminate\Notifications\ChannelManager | |
| Password | Illuminate\Auth\Passwords\PasswordBrokerManager | auth.password |
| Password(实例) | Illuminate\Auth\Passwords\PasswordBroker | auth.password.broker |
| Queue | Illuminate\Queue\QueueManager | queue |
| Queue(实例) | Illuminate\Contracts\Queue\Queue | queue.connection |
| Queue(基类) | Illuminate\Queue\Queue | |
| Redirect | Illuminate\Routing\Redirector | redirect |
| Redis | Illuminate\Redis\RedisManager | redis |
| Redis(实例) | Illuminate\Redis\Connections\Connection | redis.connection |
| Request | Illuminate\Http\Request | request |
| Response | Illuminate\Contracts\Routing\ResponseFactory | |
| Response(实例) | Illuminate\Http\Response | |
| Route | Illuminate\Routing\Router | router |
| Schema | Illuminate\Database\Schema\Builder | |
| Session | Illuminate\Session\SessionManager | session |
| Session(实例) | Illuminate\Session\Store | session.store |
| Storage | Illuminate\Filesystem\FilesystemManager | filesystem |
| Storage (实例) | Illuminate\Contracts\Filesystem\Filesystem | filesystem.disk |
| URL | Illuminate\Routing\UrlGenerator | url |
| Validator | Illuminate\Validation\Factory | validator |
| Validator(实例) | Illuminate\Validation\Validator | |
| View | Illuminate\View\Factory | view |
| View(实例) | Illuminate\View\View |


2 条回复