You are here
马哥 30_02 _tcp_wrapper&xinetd 有大用
Linux
standalone
transient
transient由xinetd控制,
xinetd: 超级守护进程 最初是 inetd, internet服务 x:extended 超级的意思
xinetd --> (n个非独立守护进程)
/etc/xinetd.conf
/etc/xinetd.d/* 关于各个非独立守护进程的配置,是主配置文件 /etc/xinetd.conf 的一个片断
xinetd 本身不提供服务的 ,,为其它 非独立守护进程 提供服务的
[root@mail ~]# ll /etc/xinetd.conf
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1001 2013-04-23 /etc/xinetd.conf
[root@mail ~]#
[root@mail ~]# ll /etc/xinetd.d
总计 176
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1157 2013-04-23 chargen-dgram
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1159 2013-04-23 chargen-stream
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1157 2013-04-23 daytime-dgram
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1159 2013-04-23 daytime-stream
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1157 2013-04-23 discard-dgram
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1159 2013-04-23 discard-stream
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1148 2013-04-23 echo-dgram
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1150 2013-04-23 echo-stream
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 323 2013-06-06 eklogin
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 347 2013-06-06 ekrb5-telnet
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 326 2013-06-06 gssftp
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 310 2013-06-06 klogin
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 323 2013-06-06 krb5-telnet
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 308 2013-06-06 kshell
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 722 2012-10-16 rmcp
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 317 2004-09-09 rsync
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 366 08-20 15:30 swat
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1212 2013-04-23 tcpmux-server
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 302 08-23 17:43 telnet # 这里除了telnet swat等其它的基本都是安装xinet后生成的软件
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 510 2009-05-19 tftp
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1149 2013-04-23 time-dgram
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1150 2013-04-23 time-stream
[root@mail ~]#
/etc/xinetd.conf
主要由两部分组成
1)全局配置 (服务的默认配置)
2)服务配置
service <service_name>
{
<attribute> <assign_op> <value> <value> ...
}
service 是关键字
<service_name> 是服务的名称
assign_op 就是赋值操作符
SYSLOG:专门用于记录日志的服务(syslogd klogd) syslogd:system logd 记录系统日志,,,klogd:kernel logd 记录内核日志
daemon:叫子进程,子设备,facility
info (debug) info 是可以省略的,表示记录的日志级别,debug级别越低,记录的越详细,
记录日志太详细,性能会极大的下降,因为会产生大量的磁盘io操作(磁盘io操作的速度会很慢)
FILE 表示把日志记录入某文件,可以软限制大小,硬限制大小
(The first limit is a soft one;
xinetd will log a message the first time this
limit is exceeded (if xinetd logs to syslog,
the message will be sent at the alert priority
level) )
(The second limit is a hard limit;
xinetd will stop logging for the affected ser-
vice (if the log file is a common log file,
then more than one service may be affected) and
will log a message about this (if xinetd logs
to syslog, the message will be sent at the
alert priority level).)
例 logtype FILE /var/log/xinetd.log
log_on_success determines what information is logged when a server is
started and when that server exits (the service id is
always included in the log entry). Any combination of
the following values may be specified:
PID logs the server process id (if the service
is implemented by xinetd without forking
another process the logged process id will
be 0)
HOST logs the remote host address
USERID logs the user id of the remote user using
the RFC 1413 identification protocol.
This option is available only for multi-
threaded stream services. #登录的用户id
EXIT logs the fact that a server exited along
with the exit status or the termination
signal (the process id is also logged if
the PID option is used) #退出时候的服务器退出信息
DURATION logs the duration of a service session # DURATION 是持续的意思 比如登录telnet时,之间发生的命令,全都记录下来
TRAFFIC logs the total bytes in and out for a
redirected service. #表示流量
log_on_failure determines what information is logged when a server
cannot be started (either because of a lack of
resources or because of access control restrictions).
The service id is always included in the log entry
along with the reason for failure. Any combination of
the following values may be specified:
HOST logs the remote host address.
USERID logs the user id of the remote user using
the RFC 1413 identification protocol.
This option is available only for multi-
threaded stream services.
ATTEMPT logs the fact that a failed attempt was
made (this option is implied by all oth-
ers). #登录尝试
[root@mail ~]# vim /etc/xinetd.conf
defaults #默认配置,全局配置
{
# enabled =
# disabled =
# Define general logging characteristics.
log_type = SYSLOG daemon info
log_on_failure = HOST # 登录失败的时候,记录HOST客户端主机信息
log_on_success = PID HOST DURATION EXIT #登录成功时记录信息,,PID 表示进程 id号,HOST表示客户端的ip地址,,DURATION 表示持续时间的信息 EXIT 表示退出信息
}
includedir /etc/xinetd.d
[root@mail ~]# service syslog status
syslogd (pid 3307) 正在运行...
klogd (pid 3310) 正在运行...
[root@mail ~]#
[root@mail ~]# man xinetd.conf
.......................
log_type determines where the service log output is sent. There
are two formats:
SYSLOG syslog_facility [syslog_level]
The log output is sent to syslog at the speci-
fied facility. Possible facility names include:
daemon, auth, authpriv, user, mail, lpr, news,
uucp, ftp local0-7. Possible level names
include: emerg, alert, crit, err, warning,
notice, info, debug. If a level is not
present, the messages will be recorded at the
info level.
FILE file [soft_limit [hard_limit]] #可以明确说明写在哪个文件当中
The log output is appended to file which will
be created if it does not exist. Two limits on
the size of the log file can be optionally
specified. The first limit is a soft one;
xinetd will log a message the first time this
limit is exceeded (if xinetd logs to syslog,
the message will be sent at the alert priority
level). The second limit is a hard limit;
xinetd will stop logging for the affected ser-
vice (if the log file is a common log file,
then more than one service may be affected) and
will log a message about this (if xinetd logs
to syslog, the message will be sent at the
alert priority level). If a hard limit is not
specified, it defaults to the soft limit
increased by 1% but the extra size must be
within the parameters LOG_EXTRA_MIN and
LOG_EXTRA_MAX which default to 5K and 20K
respectively (these constants are defined in
xconfig.h).
[root@mail ~]# cd /etc/xinetd.d/
[root@mail xinetd.d]#
[root@mail xinetd.d]# ls
chargen-dgram discard-stream gssftp rsync time-dgram
chargen-stream echo-dgram klogin swat time-stream
daytime-dgram echo-stream krb5-telnet tcpmux-server
daytime-stream eklogin kshell telnet
discard-dgram ekrb5-telnet rmcp tftp
[root@mail xinetd.d]#
[root@mail xinetd.d]# vim telnet
# default: on
# description: The telnet server serves telnet sessions; it uses \
# unencrypted username/password pairs for authentication.
service telnet # 服务名称 telnet 与文件名一般要保持一致
{
disable = no #表示启用
flags = REUSE
socket_type = stream
wait = no
user = root
server = /usr/sbin/in.telnetd
log_on_failure += USERID
}
[root@mail xinetd.d]# vim rsync
# default: off
# description: The rsync server is a good addition to an ftp server, as it \
# allows crc checksumming etc.
service rsync
{
disable = yes
socket_type = stream
wait = no
user = root
server = /usr/bin/rsync
server_args = --daemon
log_on_failure += USERID
}
[root@mail xinetd.d]# vim telnet
# default: on
# description: The telnet server serves telnet sessions; it uses \
# unencrypted username/password pairs for authentication.
service telnet # 服务名称 telnet 与文件名一般要保持一致
{
disable = yes #表示禁用
flags = REUSE
socket_type = stream
wait = no
user = root
server = /usr/sbin/in.telnetd
log_on_failure += USERID
}
重启 xinetd 或者重新装载 xinetd
[root@mail xinetd.d]# service xinetd restart ( service xinetd reload )
停止 xinetd: [确定]
启动 xinetd: [确定]
[root@mail xinetd.d]#
[root@mail xinetd.d]# netstat -tnlp # 没有 23号端口了
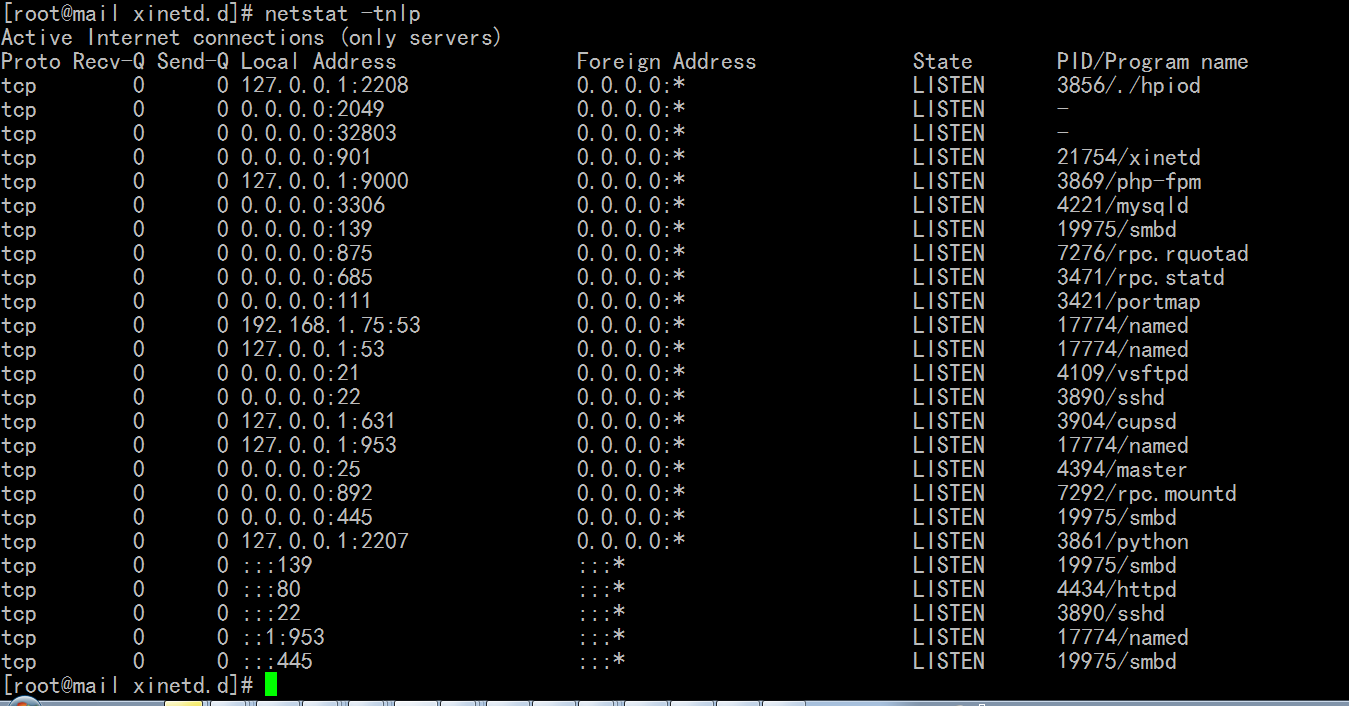
启动 telnet ,,chkconfig telnet on 命令 ,相当于修改了 /etc/xinetd.d/telnet 文件中的 disable = no
[root@mail xinetd.d]# chkconfig telnet on
[root@mail xinetd.d]# cat telnet
# default: on
# description: The telnet server serves telnet sessions; it uses \
# unencrypted username/password pairs for authentication.
service telnet
{
disable = no #变成了no
flags = REUSE
socket_type = stream
wait = no
user = root
server = /usr/sbin/in.telnetd
log_on_failure += USERID
}
[root@mail xinetd.d]#
关闭 telnet ,,chkconfig telnet off 命令 ,相当于修改了 /etc/xinetd.d/telnet 文件中的 disable = yes
[root@mail xinetd.d]# chkconfig telnet off
[root@mail xinetd.d]# cat telnet
# default: on
# description: The telnet server serves telnet sessions; it uses \
# unencrypted username/password pairs for authentication.
service telnet
{
disable = yes #它变成了 yes
flags = REUSE
socket_type = stream
wait = no
user = root
server = /usr/sbin/in.telnetd
log_on_failure += USERID
}
[root@mail xinetd.d]#
[root@mail xinetd.d]# chkconfig --level 2345 telnet on # 开启非独立守护进程( telnet ),指定级别是无用的
[root@mail xinetd.d]#
[root@mail xinetd.d]# chkconfig --list
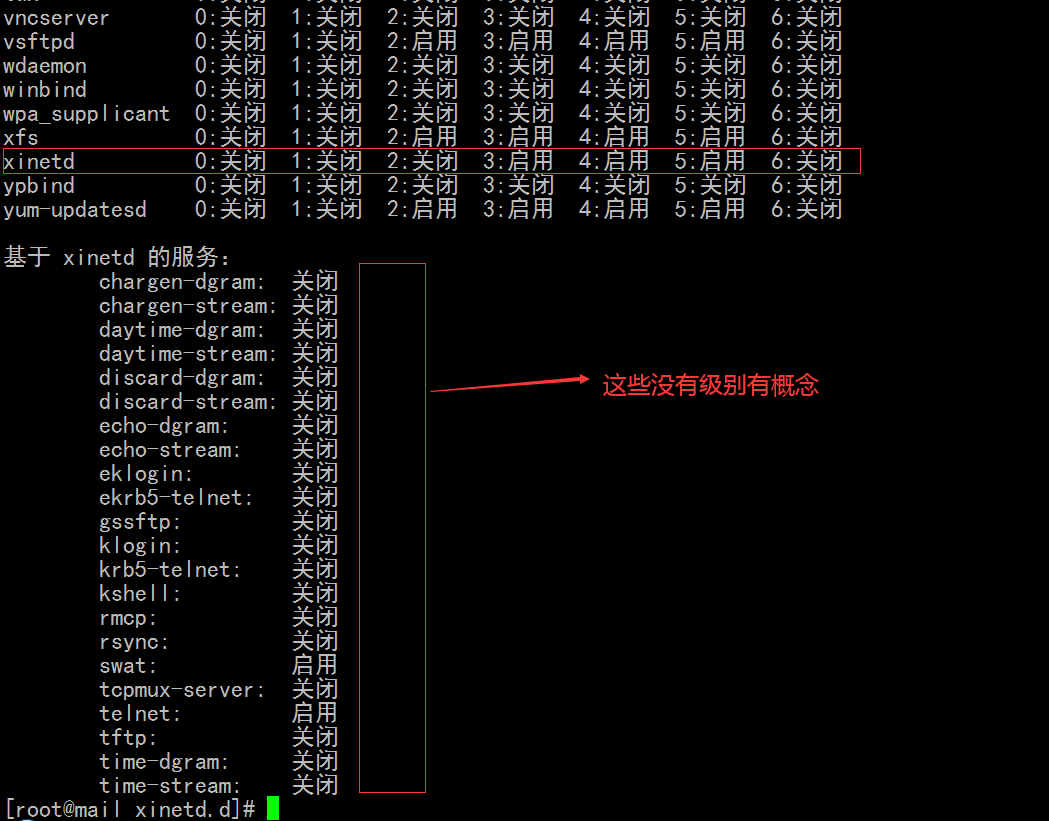
[root@mail xinetd.d]# pwd
/etc/xinetd.d
[root@mail xinetd.d]# vim telnet
# default: on
# description: The telnet server serves telnet sessions; it uses \
# unencrypted username/password pairs for authentication.
service telnet
{
disable = no
flags = REUSE #标志,reuse 就是可被重用的,可被多次访问
socket_type = stream #套接字类型,服务本身所基于的协议 一般是三种 tcp(流)/udp(数据报文)/rpc(远程过程调用) tcp:stream流表示tcp协议 ,udp:dgram (data_gram)数据报文,表示udp协议 rpc:远程过程调用(portmap是提供rpc服务的)
wait = no # 后一个用户是不是等待前一个用户连接结束后再连入的;;udp是无法等待的,因为它udp数据流不受连接控制,tcp等不等待是根据需要来定义的
user = root #表示运行 telnet 服务的用户的身份
server = /usr/sbin/in.telnetd #定义的应用程序服务是谁,用哪个应用程序来启动 telnet 的,它是一个二进制程序文件
log_on_failure += USERID # 失败的时候记录的日志信息的格式, 加等于 += 表示在默认值的基础上再增加一个选项 减等于号 表示去掉默认配置中的某一项 等于号表示覆盖默认配置
# 这里假如没有 log_type ,表示使用 xinetd.conf里的默认设置 这里即syslog日志,即通常在 /var/log/message中,但不是一定在 这个文件中
log_type = FILE /var/log/telnet.log # 有了 log_type ,会覆盖默认
}
portmap-->提供 rpc服务
nfs利用 <-- rpc服务
[root@mail xinetd.d]# pwd
/etc/xinetd.d
[root@mail xinetd.d]# man xinetd.conf
socket_type Possible values for this attribute include:
stream stream-based service
dgram datagram-based service
raw service that requires direct access to IP
seqpacket service that requires reliable sequential
datagram transmission
[root@mail xinetd.d]# tail /var/log/messages
Aug 24 16:07:02 mail last message repeated 52 times
Aug 24 16:08:03 mail last message repeated 50 times
Aug 24 16:09:07 mail last message repeated 40 times
Aug 24 16:10:10 mail last message repeated 42 times
Aug 24 16:11:31 mail last message repeated 30 times
Aug 24 16:12:33 mail last message repeated 38 times
Aug 24 16:13:39 mail last message repeated 45 times
Aug 24 16:14:43 mail last message repeated 26 times
Aug 24 16:16:06 mail last message repeated 16 times
Aug 24 16:17:18 mail last message repeated 24 times
[root@mail xinetd.d]#
[root@mail xinetd.d]# vim telnet
# default: on
# description: The telnet server serves telnet sessions; it uses \
# unencrypted username/password pairs for authentication.
service telnet
{
disable = no
flags = REUSE
socket_type = stream
wait = no
user = root
server = /usr/sbin/in.telnetd
log_type = FILE /var/log/telnet.log #加上这行 这里不做软限制,硬限制了
log_on_failure += USERID
}
重启 xinetd 服务
[root@mail xinetd.d]# service xinetd restart
停止 xinetd: [确定]
启动 xinetd: [确定]
[root@mail xinetd.d]#
[root@mail xinetd.d]# vim /etc/hosts.allow # 把 tcp wrapper 的 控制去掉
#
# hosts.allow This file describes the names of the hosts which are
# allowed to use the local INET services, as decided
# by the '/usr/sbin/tcpd' server.
#
#in.telnetd: 192.168.1. EXCEPT 192.168.1.251 :spawn echo "`date`, login attempt from %c to %s." >> /var/log/tcpwrapper.log # 把 tcp wrapper 的 控制去掉
~
[root@mail xinetd.d]# vim /etc/hosts.deny # 把这里 tcp wrapper 的 控制也去掉
#
# hosts.deny This file describes the names of the hosts which are
# *not* allowed to use the local INET services, as decided
# by the '/usr/sbin/tcpd' server.
#
#in.telnetd: ALL :spawn echo "`date`, login attempt from %h " >> /var/log/tcpwrapper.log # 把这里 tcp wrapper 的 控制也去掉
在 windows 上 用 telnet 登进服务器 # telnet 192.168.1.75 23 (端口号23可以省略)
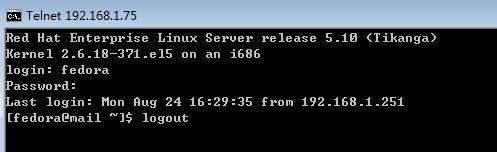
看看服务器 有没有telnet 日志
[root@mail xinetd.d]# tail /var/log/telnet.log
20/8/24@16:28:39: START: telnet pid=21880 from=192.168.1.251
20/8/24@16:28:39: FAIL: telnet libwrap from=192.168.1.251
20/8/24@16:28:39: EXIT: telnet status=0 pid=21880 duration=0(sec)
20/8/24@16:28:48: START: telnet pid=21884 from=192.168.1.251
20/8/24@16:28:48: FAIL: telnet libwrap from=192.168.1.251
20/8/24@16:28:48: EXIT: telnet status=0 pid=21884 duration=0(sec)
20/8/24@16:29:17: START: telnet pid=21888 from=192.168.1.251
[root@mail xinetd.d]#
讲解xinetd的配置文件的几个属性
访问控制:
only_from = # 仅允许 仅允许来自哪些客户机的请求访问的
IP: 172.16.100.200
NETWORK: 172.16.0.0/16 , 或 172.16.0.0/255.255.0.0
HOSTNAME: FQDN 例如 www.magedu.com (涉及到dns解析,浪费时间性能,不建议)
DOMAIN: .magedu.com (涉及到dns解析,浪费时间性能,不建议)
no_access = # 仅拒绝 不允许谁访问 接受的格式与 only_from 是一样的
only_from,no_access 谁的匹配范围越小(谁最佳),谁生效,,,,一般情况下不要一块来用,万一在一块用时,最好自己试一下,谁生效
时间控制 ( time = 好像要用 access_time )
access_times = hh:mm-hh:mm
hh:0-23
mm:0-59
监听的地址 (提供服务的地址):
bind = # 一般用 bind 吧
或者 interface =
可以定义资源访问法则,
比如可以定义这个端口(这个服务)所能接受的连接数,超出连接数之后的用户请求如何处理
资源访问控制
cps ( collections per second) 控制每秒钟入站连接的个数 (在数据量大时,很有效果的)
两个参数:
每秒入站连接数的最大值 临时禁用的时长
per_source = 每个客户端ip最多并发发起几个连接请求的
instances = 用于定义服务最多允许多少个用户同时连进来?最大同时连接数
cps , per_source , instances 通常结合起来作为资源访问控制的指令
向启动的server传递参数:
server_args = 比如 -c 文件路径 ; -d 什么什么的
port = #定义某个服务所监听的端口,如果不定义,就使用此服务约定俗成的端口
比如 telnet 使用的是 23号 端口
比如 如下 23 端口 可以省掉

banner 横幅, 客户端登录时就看到的内容(写在文件里的)
[root@mail xinetd.d]# vim telnet
# default: on
# description: The telnet server serves telnet sessions; it uses \
# unencrypted username/password pairs for authentication.
service telnet
{
disable = no
flags = REUSE
socket_type = stream
wait = no
user = root
server = /usr/sbin/in.telnetd
only_from = 192.168.1.0/24 #增加这个 仅允许这个网段的主机访问telnet服务
log_type = FILE /var/log/telnet.log
log_on_failure += USERID
}
~
重启下 xinetd 服务
[root@mail xinetd.d]# service xinetd restart
停止 xinetd: [确定]
启动 xinetd: [确定]
[root@mail xinetd.d]#
在 windows 上 可以登进

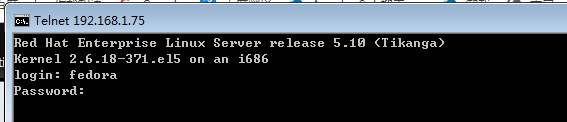
[root@mail xinetd.d]# pwd
/etc/xinetd.d
[root@mail xinetd.d]#
[root@mail xinetd.d]# vim telnet
# default: on
# description: The telnet server serves telnet sessions; it uses \
# unencrypted username/password pairs for authentication.
service telnet
{
disable = no
flags = REUSE
socket_type = stream
wait = no
user = root
server = /usr/sbin/in.telnetd
only_from = 192.168.1.0/24
no_access = 192.168.1.251 # 只增加这个
log_type = FILE /var/log/telnet.log
log_on_failure += USERID
}
~
重启下 xinetd 服务
[root@mail xinetd.d]# service xinetd restart
停止 xinetd: [确定]
启动 xinetd: [确定]
[root@mail xinetd.d]#
windows 不能访问了
直接跳到如下图的样子了
[root@mail xinetd.d]# vim telnet
# default: on
# description: The telnet server serves telnet sessions; it uses \
# unencrypted username/password pairs for authentication.
service telnet
{
disable = no
flags = REUSE
socket_type = stream
wait = no
user = root
server = /usr/sbin/in.telnetd
only_from = 192.168.1.0/24
access_times = 16:00-17:00
log_type = FILE /var/log/telnet.log
log_on_failure += USERID
}
[root@mail xinetd.d]# vim telnet
# default: on
# description: The telnet server serves telnet sessions; it uses \
# unencrypted username/password pairs for authentication.
service telnet
{
disable = no
flags = REUSE
socket_type = stream
wait = no
user = root
server = /usr/sbin/in.telnetd
only_from = 192.168.1.0/24
access_times = 17:00-18:00 # 加上它,仅在 17:00至18:00可以访问 去掉 no_access = 192.168.1.251 的配置
log_type = FILE /var/log/telnet.log
log_on_failure += USERID
}
重启下 xinetd 服务
[root@mail xinetd.d]# service xinetd restart
停止 xinetd: [确定]
启动 xinetd: [确定]
现在是 17:30 分 ,,,在 windows 上 可以登进


[root@mail xinetd.d]# vim telnet
# default: on
# description: The telnet server serves telnet sessions; it uses \
# unencrypted username/password pairs for authentication.
service telnet
{
disable = no
flags = REUSE
socket_type = stream
wait = no
user = root
server = /usr/sbin/in.telnetd
only_from = 192.168.1.0/24
access_times = 16:00-17:00 # 仅改了下时间
log_type = FILE /var/log/telnet.log
log_on_failure += USERID
}
重启下 xinetd 服务
[root@mail xinetd.d]# service xinetd restart
停止 xinetd: [确定]
启动 xinetd: [确定]
现在是 17:30 分 ,,windows 不能访问了

直接跳到如下图的样子了

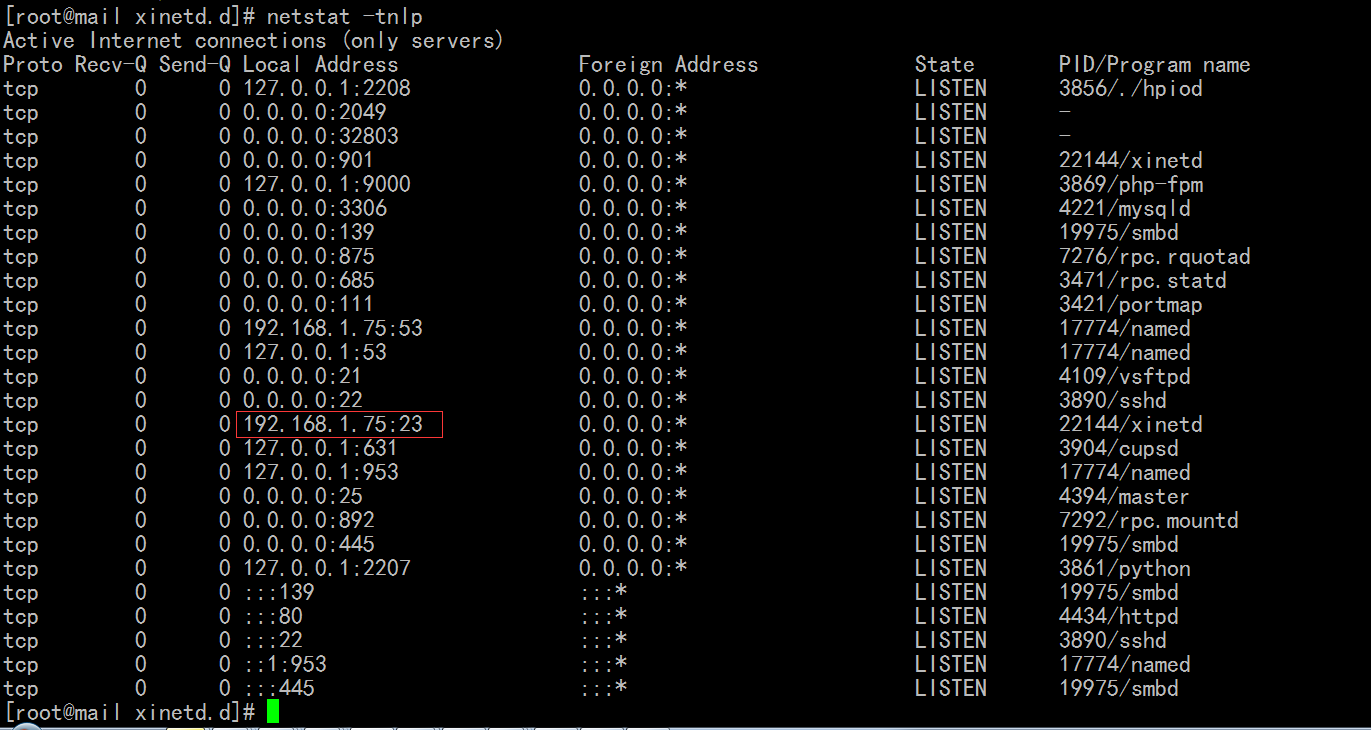
一个电脑可能有多个ip ,这里 telnet 23号端口 监听在 0.0.0.0 上 (即所有地址)
[root@mail xinetd.d]# netstat -tnlp
Active Internet connections (only servers)
Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State PID/Program name
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:2208 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 3856/./hpiod
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:2049 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN -
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:32803 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN -
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:901 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 22101/xinetd
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:9000 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 3869/php-fpm
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:3306 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 4221/mysqld
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:139 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 19975/smbd
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:875 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 7276/rpc.rquotad
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:685 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 3471/rpc.statd
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:111 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 3421/portmap
tcp 0 0 192.168.1.75:53 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 17774/named
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:53 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 17774/named
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:21 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 4109/vsftpd
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 3890/sshd
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:23 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 22101/xinetd
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:631 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 3904/cupsd
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:953 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 17774/named
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:25 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 4394/master
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:892 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 7292/rpc.mountd
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:445 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 19975/smbd
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:2207 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 3861/python
tcp 0 0 :::139 :::* LISTEN 19975/smbd
tcp 0 0 :::80 :::* LISTEN 4434/httpd
tcp 0 0 :::22 :::* LISTEN 3890/sshd
tcp 0 0 ::1:953 :::* LISTEN 17774/named
tcp 0 0 :::445 :::* LISTEN 19975/smbd
[root@mail xinetd.d]#
重启下 xinetd 服务
[root@mail xinetd.d]# service xinetd restart
停止 xinetd: [确定]
启动 xinetd: [确定]
[root@mail xinetd.d]#
[root@mail xinetd.d]# vim telnet
# default: on
# description: The telnet server serves telnet sessions; it uses \
# unencrypted username/password pairs for authentication.
service telnet
{
disable = no
flags = REUSE
socket_type = stream
wait = no
user = root
server = /usr/sbin/in.telnetd
only_from = 192.168.1.0/24
access_times = 16:00-17:00
bind = 192.168.1.75 # 仅增加这行,表示只在这个地址上提供telnet服务
log_type = FILE /var/log/telnet.log
log_on_failure += USERID
}
[root@mail xinetd.d]# netstat -tnlp # 这里看到只在 192.168.1.75 上监听了
[root@mail xinetd.d]# man xinetd.conf
cps Limits the rate of incoming connections. Takes two
arguments. The first argument is the number of con-
nections per second to handle. If the rate of incom-
ing connections is higher than this, the service will
be temporarily disabled. The second argument is the
number of seconds to wait before re-enabling the ser-
vice after it has been disabled. The default for this
setting is 50 incoming connections and the interval is
10 seconds.
[root@mail xinetd.d]# vim telnet
# default: on
# description: The telnet server serves telnet sessions; it uses \
# unencrypted username/password pairs for authentication.
service telnet
{
disable = no
flags = REUSE
socket_type = stream
wait = no
user = root
server = /usr/sbin/in.telnetd
only_from = 192.168.1.0/24
access_times = 0:00-23:59 # 这个时间也改下吧
bind = 192.168.1.75
cps = 1 10 #仅增加这行,1 表示每秒钟最大连接数是1个,超过1个后telnet服务等待10秒钟
log_type = FILE /var/log/telnet.log
log_on_failure += USERID
}
重启下 xinetd 服务
[root@mail xinetd.d]# service xinetd restart
停止 xinetd: [确定]
启动 xinetd: [确定]
[root@mail xinetd.d]#
在 windows 上 可以登进了 (但是马哥是 连不上)


[root@mail xinetd.d]# vim telnet
# default: on
# description: The telnet server serves telnet sessions; it uses \
# unencrypted username/password pairs for authentication.
service telnet
{
disable = no
flags = REUSE
socket_type = stream
wait = no
user = root
server = /usr/sbin/in.telnetd
only_from = 192.168.1.0/24
access_times = 0:00-23:59
bind = 192.168.1.75
cps = 2 10 # 马哥 改最大连接数改成 2 试试
log_type = FILE /var/log/telnet.log
log_on_failure += USERID
}
重启下 xinetd 服务
[root@mail xinetd.d]# service xinetd restart
停止 xinetd: [确定]
启动 xinetd: [确定]
[root@mail xinetd.d]#
改成 2 后,马哥 在 windows 上 可以登进了


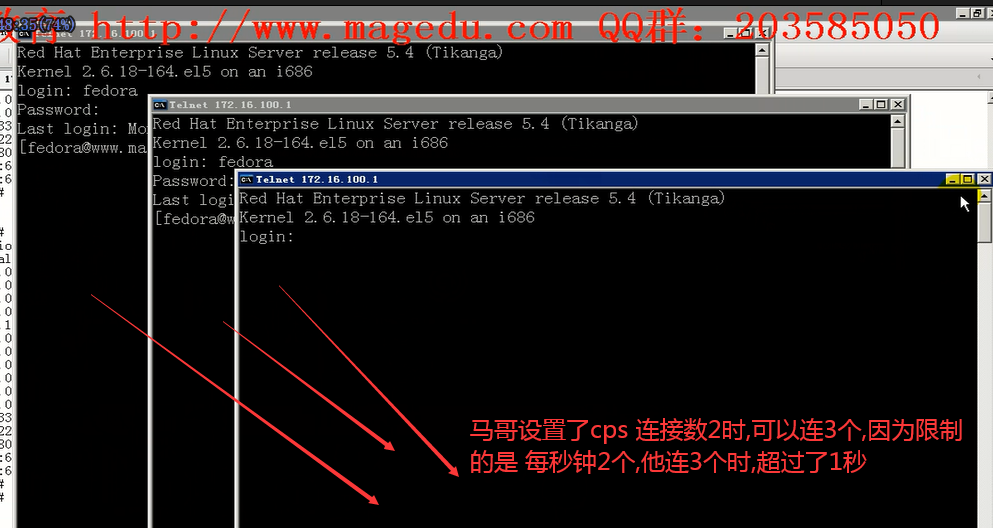
[root@mail xinetd.d]# man xinetd.conf
per_source Takes an integer or "UNLIMITED" as an argument. This
specifies the maximum instances of this service per
source IP address. This can also be specified in the
defaults section.
[root@mail xinetd.d]# vim telnet
# default: on
# description: The telnet server serves telnet sessions; it uses \
# unencrypted username/password pairs for authentication.
service telnet
{
disable = no
flags = REUSE
socket_type = stream
wait = no
user = root
server = /usr/sbin/in.telnetd
only_from = 192.168.1.0/24
access_times = 0:00-23:59
bind = 192.168.1.75
per_source = 1 # 只增加这行,这里表示每个单独的ip只允许发送一个连接请求 去掉了cps = 1 10
log_type = FILE /var/log/telnet.log
log_on_failure += USERID
}
重启下 xinetd 服务
[root@mail xinetd.d]# service xinetd restart
停止 xinetd: [确定]
启动 xinetd: [确定]
第一个telnet 可以登进


第二个telnet windows 不能访问了

直接跳到如下图的样子了

[root@mail xinetd.d]# vim telnet
# default: on
# description: The telnet server serves telnet sessions; it uses \
# unencrypted username/password pairs for authentication.
service telnet
{
disable = no
flags = REUSE
socket_type = stream
wait = no
user = root
server = /usr/sbin/in.telnetd
only_from = 192.168.1.0/24
access_times = 0:00-23:59
bind = 192.168.1.75
per_source = 1
cps = 25 30 #加上这行
log_type = FILE /var/log/telnet.log
log_on_failure += USERID
}
[root@mail xinetd.d]# man xinetd.conf
.......................
instances determines the number of servers that can be simulta-
neously active for a service (the default is no
limit). The value of this attribute can be either a
number or UNLIMITED which means that there is no
limit.
server determines the program to execute for this service. #启动这个服务对应的二进制文件
server_args determines the arguments passed to the server. In con-
trast to inetd, the server name should not be included
in server_args. # 启动这个服务所传进去的参数
.......................
[root@mail xinetd.d]# vim telnet
# default: on
# description: The telnet server serves telnet sessions; it uses \
# unencrypted username/password pairs for authentication.
service telnet
{
disable = no
flags = REUSE
socket_type = stream
wait = no
user = root
server = /usr/sbin/in.telnetd # 有时想在后面 传 -c -d 之类的参数,使用 server_args 来传参
only_from = 192.168.1.0/24
access_times = 0:00-23:59
bind = 192.168.1.75
per_source = 1
cps = 25 30
log_type = FILE /var/log/telnet.log
log_on_failure += USERID
}
[root@mail ~]# man xinetd.conf
banner Takes the name of a file to be splatted at the remote
host when a connection to that service is established.
This banner is printed regardless of access control.
It should *always* be printed when a connection has
been made. xinetd outputs the file as-is, so you must
ensure the file is correctly formatted for the ser-
vice’s protocol. In paticular, if the protocol
requires CR-LF pairs for line termination, you must
supply them.
[root@mail xinetd.d]# vim telnet
# default: on
# description: The telnet server serves telnet sessions; it uses \
# unencrypted username/password pairs for authentication.
service telnet
{
disable = no
flags = REUSE
socket_type = stream
wait = no
user = root
server = /usr/sbin/in.telnetd
only_from = 192.168.1.0/24
access_times = 0:00-23:59
bind = 192.168.1.75
per_source = 1
cps = 25 30
banner = /etc/telnet.banner # 仅增加这行,显示横幅
log_type = FILE /var/log/telnet.log
log_on_failure += USERID
}
[root@mail xinetd.d]# vim /etc/telnet.banner
Welcome to our telnet server.....
重启 xinetd 或者重新装载 xinetd
[root@mail xinetd.d]# service xinetd restart ( service xinetd reload )
停止 xinetd: [确定]
启动 xinetd: [确定]
windows 用 telnet 登录

可以看到 banner 文件里的文字信息
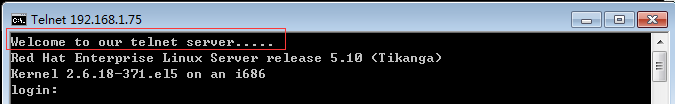
其实 登录后 还会看到 /etc/issue 里的内容(其实看到的是/etc/issue.net 里的内容 )
[root@mail xinetd.d]# cat /etc/issue #它是通过本地登录显示的banner信息
Red Hat Enterprise Linux Server release 5.10 (Tikanga)
Kernel \r on an \m
[root@mail xinetd.d]#
[root@mail xinetd.d]# cat /etc/issue.net # 它与 /etc/issue 内容差不多吧 # 事实上 telnet登录后显示的是 /etc/issue.net 里的内容 #它是通过网络登录显示的banner信息
Red Hat Enterprise Linux Server release 5.10 (Tikanga)
Kernel \r on an \m
[root@mail xinetd.d]#
我们可以通过 iptables,tcp wrapper ,xinetd 三种方法 控制服务的访问
有些特定的功能可能只有某一种方法才能实现控制

[root@mail xinetd.d]# pwd
/etc/xinetd.d
[root@mail xinetd.d]#
[root@mail xinetd.d]# vim rsync
# default: off
# description: The rsync server is a good addition to an ftp server, as it \
# allows crc checksumming etc.
service rsync
{
disable = no
socket_type = stream
wait = no
user = root
server = /usr/bin/rsync
server_args = --daemon
log_on_failure += USERID
only_from = 192.168.1.0/24
no_access = 192.168.1.251
bind = 192.168.1.75
instances = 3
per_source = 2
}
~
重启 xinetd 或者重新装载 xinetd
[root@mail xinetd.d]# service xinetd restart ( service xinetd reload )
停止 xinetd: [确定]
启动 xinetd: [确定]
rsync 监听在 873 的端口上
[root@mail xinetd.d]# netstat -tnlp
Active Internet connections (only servers)
Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State PID/Program name
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:2208 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 3856/./hpiod
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:2049 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN -
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:32803 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN -
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:901 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 22502/xinetd
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:9000 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 3869/php-fpm
tcp 0 0 192.168.1.75:873 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 22502/xinetd
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:3306 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 4221/mysqld
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:139 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 19975/smbd
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:875 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 7276/rpc.rquotad
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:685 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 3471/rpc.statd
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:111 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 3421/portmap
tcp 0 0 192.168.1.75:53 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 17774/named
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:53 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 17774/named
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:21 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 4109/vsftpd
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 3890/sshd
tcp 0 0 192.168.1.75:23 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 22502/xinetd
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:631 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 3904/cupsd
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:953 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 17774/named
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:25 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 4394/master
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:892 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 7292/rpc.mountd
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:445 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 19975/smbd
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:2207 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 3861/python
tcp 0 0 :::139 :::* LISTEN 19975/smbd
tcp 0 0 :::80 :::* LISTEN 4434/httpd
tcp 0 0 :::22 :::* LISTEN 3890/sshd
tcp 0 0 ::1:953 :::* LISTEN 17774/named
tcp 0 0 :::445 :::* LISTEN 19975/smbd
[root@mail xinetd.d]#
rsync ( remote sync )服务的主要目的是提供rsync文件同步服务的
