ATTACK MODE b: Beacon Flooding
Sends beacon frames to generate fake APs at clients.
This can sometimes crash network scanners and drivers!
-n <ssid>
Use SSID <ssid> instead of randomly generated ones
-a
Use also non-printable caracters in generated SSIDs
and create SSIDs that break the 32-byte limit
-f <filename>
Read SSIDs from file
-v <filename>
Read MACs and SSIDs from file. See example file!
-t <adhoc>
-t 1 = Create only Ad-Hoc network
-t 0 = Create only Managed (AP) networks
without this option, both types are generated
-w <encryptions>
Select which type of encryption the fake networks shall have
Valid options: n = No Encryption, w = WEP, t = TKIP (WPA), a = AES (WPA2)
You can select multiple types, i.e. "-w wta" will only create WEP and WPA networks
-b <bitrate>
Select if 11 Mbit (b) or 54 MBit (g) networks are created
Without this option, both types will be used.
-m
Use valid accesspoint MAC from built-in OUI database
-h
Hop to channel where network is spoofed
This is more effective with some devices/drivers
But it reduces packet rate due to channel hopping.
-c <chan>
Create fake networks on channel <c ATTACK MODE f: Packet Fuzzer
A simple packet fuzzer with multiple packet sources
and a nice set of modifiers. Be careful!han>. If you want your card to
hop on this channel, you have to set -h option, too.
-i <HEX>
Add user-defined IE(s) in hexadecimal at the end of the tagged parameters
-s <pps>
Set speed in packets per second (Default: 50)
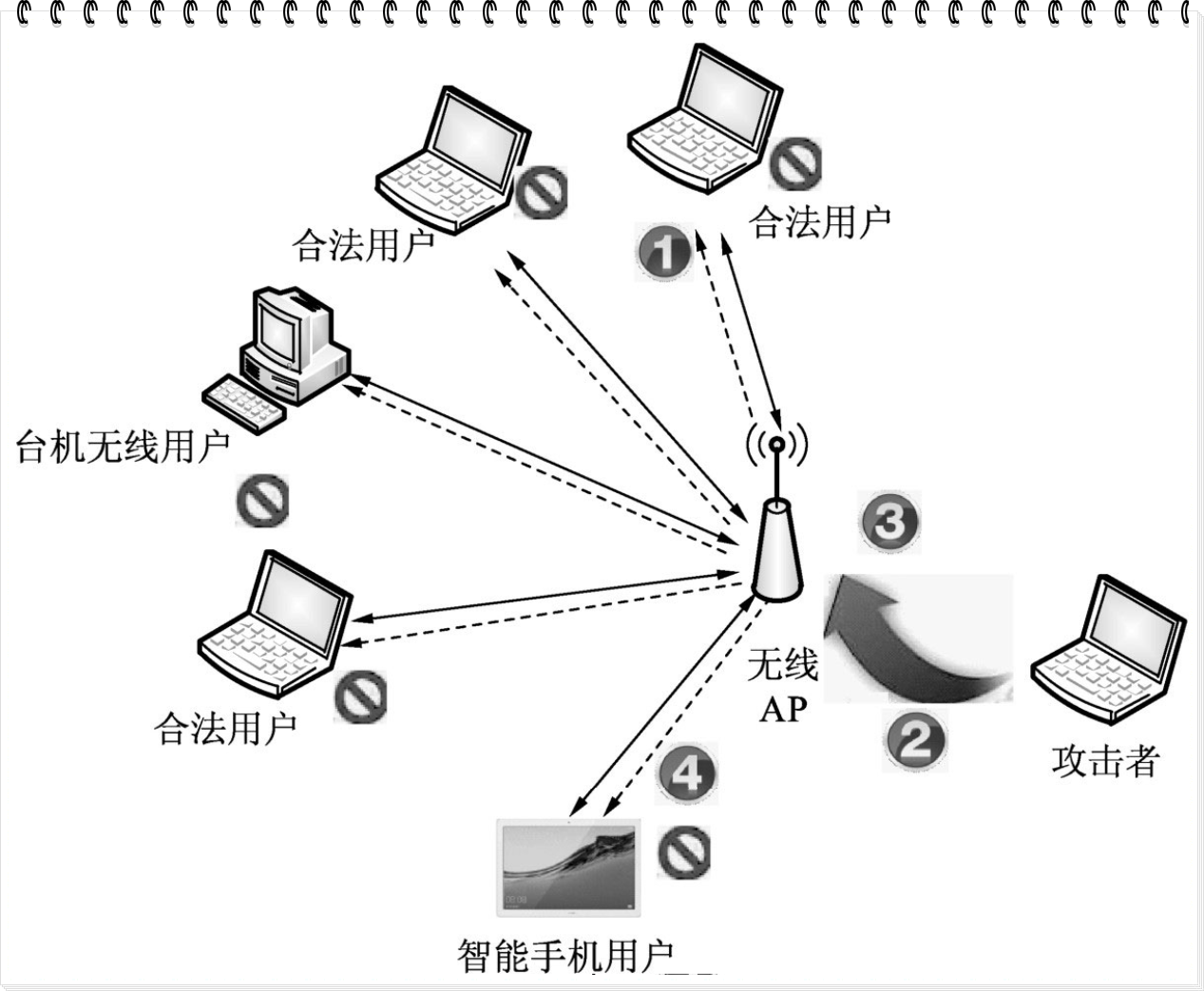
ATTACK MODE a: Authentication Denial-Of-Service
Sends authentication frames to all APs found in range.
Too many clients can freeze or reset several APs.
-a <ap_mac>
Only test the specified AP
-m
Use valid client MAC from built-in OUI database
-i <ap_mac>
Perform intelligent test on AP
This test connects clients to the AP and reinjects sniffed data to keep them alive.
-s <pps>
Set speed in packets per second (Default: unlimited)
ATTACK MODE p: SSID Probing and Bruteforcing
Probes APs and checks for answer, useful for checking if SSID has
been correctly decloaked and if AP is in your sending range.
Bruteforcing of hidden SSIDs with or without a wordlist is also available.
-e <ssid>
SSID to probe for
-f <filename>
Read SSIDs from file for bruteforcing hidden SSIDs
-t <bssid>
Set MAC address of target AP
-s <pps>
Set speed (Default: 400)
-b <character sets>
Use full Bruteforce mode (recommended for short SSIDs only!)
You can select multiple character sets at once:
* n (Numbers: 0-9)
* u (Uppercase: A-Z)
* l (Lowercase: a-z)
* s (Symbols: ASCII)
-p <word>
Continue bruteforcing, starting at <word>.
-r <channel>
Probe request tests (mod-musket)
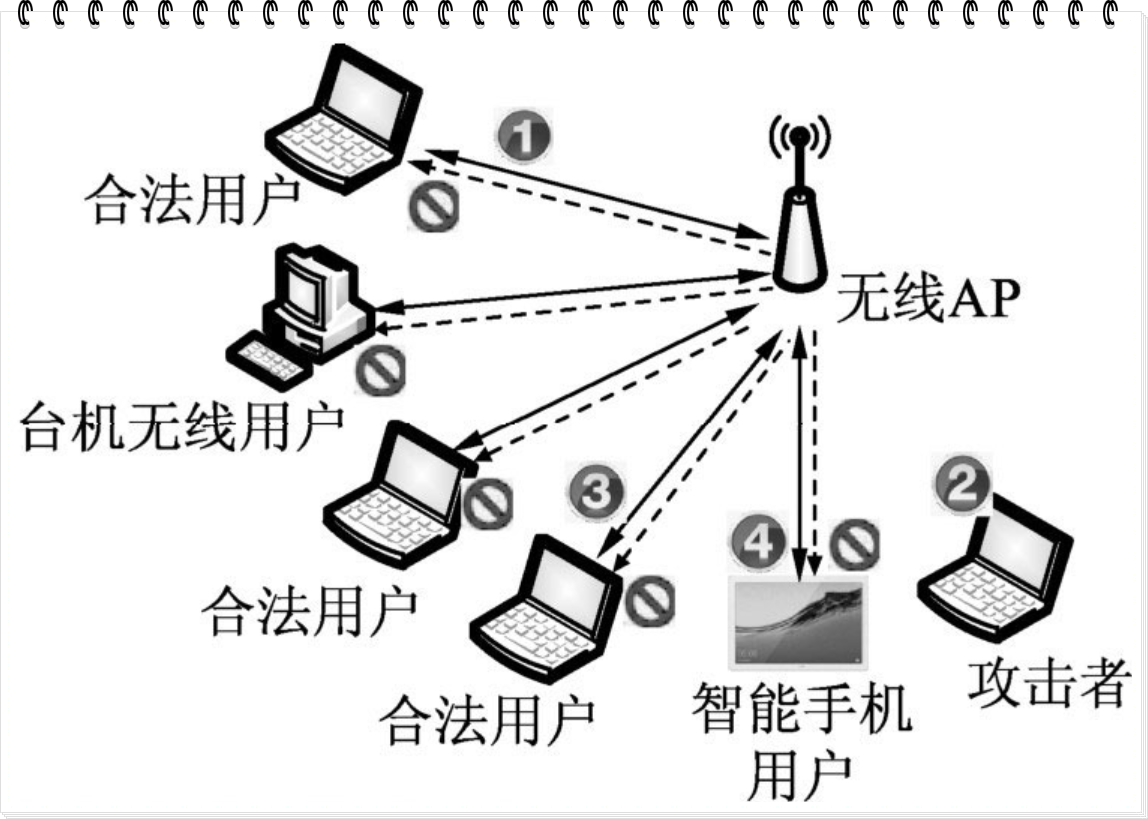
ATTACK MODE d: Deauthentication and Disassociation
Sends deauthentication and disassociation packets to stations
based on data traffic to disconnect all clients from an AP.
-w <filename>
Read file containing MACs not to care about (Whitelist mode)
-b <filename>
Read file containing MACs to run test on (Blacklist Mode)
-s <pps>
Set speed in packets per second (Default: unlimited)
-x
Enable full IDS stealth by matching all Sequence Numbers
Packets will only be sent with clients' addresses
-c [chan,chan,...,chan[:speed]]
Enable channel hopping. When -c h is given, mdk4 will hop an all
14 b/g channels. Channel will be changed every 3 seconds,
if speed is not specified. Speed value is in milliseconds!
-E <AP ESSID>
Specify an AP ESSID to attack.
-B <AP BSSID>
Specify an AP BSSID to attack.
-S <Station MAC address>
Specify a station MAC address to attack.
-W <Whitelist Station MAC address>
Specify a whitelist station MAC.
ATTACK MODE m: Michael Countermeasures Exploitation
Sends random packets or re-injects duplicates on another QoS queue
to provoke Michael Countermeasures on TKIP APs.
AP will then shutdown for a whole minute, making this an effective DoS.
-t <bssid>
Set target AP, that runs TKIP encryption
-j
Use the new QoS exploit which only needs to reinject a few packets instead
of the random packet injection, which is unreliable but works without QoS.
-s <pps>
Set speed in packets per second (Default: 400)
-w <seconds>
Wait <seconds> between each random packet burst (Default: 10)
-n <count>
Send <count> random packets per burst (Default: 70)
ATTACK MODE e: EAPOL Start and Logoff Packet Injection
Floods an AP with EAPOL Start frames to keep it busy with fake sessions
and thus disables it to handle any legitimate clients.
Or logs off clients by injecting fake EAPOL Logoff messages.
-t <bssid>
Set target WPA AP
-s <pps>
Set speed in packets per second (Default: 400)
-l
Use Logoff messages to kick clients
ATTACK MODE s: Attacks for IEEE 802.11s mesh networks
Various attacks on link management and routing in mesh networks.
Flood neighbors and routes, create black holes and divert traffic!
-f <type>
Basic fuzzing tests. Picks up Action and Beacon frames from the air, modifies and replays them:
The following modification types are implemented:
1: Replay identical frame until new one arrives (duplicate flooding)
2: Change Source and BSSID (possibly resulting in Neighbor Flooding)
3: Cut packet short, leave 802.11 header intact (find buffer errors)
4: Shotgun mode, randomly overwriting bytes after header (find bugs)
5: Skript-kid's automated attack trying all of the above randomly :)
-b <impersonated_meshpoint>
Create a Blackhole, using the impersonated_meshpoint's MAC address
mdk4 will answer every incoming Route Request with a perfect route over the impersonated node.
-p <impersonated_meshpoint>
Path Request Flooding using the impersonated_meshpoint's address
Adjust the speed switch (-s) for maximum profit!
-l
Just create loops on every route found by modifying Path Replies
-s <pps>
Set speed in packets per second (Default: 100)
-n <meshID>
Target this mesh network
ATTACK MODE w: WIDS Confusion
Confuse/Abuse Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems by
cross-connecting clients to multiple WDS nodes or fake rogue APs.
Confuses a WDS with multi-authenticated clients which messes up routing tables
-e <SSID>
SSID of target WDS network
-c [chan,chan,...,chan[:speed]]
Enable channel hopping. When -c h is given, mdk4 will hop an all
14 b/g channels. Channel will be changed every 3 seconds,
if speed is not specified. Speed value is in milliseconds!
-z
activate Zero_Chaos' WIDS exploit
(authenticates clients from a WDS to foreign APs to make WIDS go nuts)
-s <pps>
Set speed in packets per second (Default: 100)
ATTACK MODE f: Packet Fuzzer
A simple packet fuzzer with multiple packet sources
and a nice set of modifiers. Be careful!
mdk4 randomly selects the given sources and one or multiple modifiers.
-s <sources>
Specify one or more of the following packet sources:
a - Sniff packets from the air
b - Create valid beacon frames with random SSIDs and properties
c - Create CTS frames to broadcast (you can also use this for a CTS DoS)
p - Create broadcast probe requests
-m <modifiers>
Select at least one of the modifiers here:
n - No modifier, do not modify packets
b - Set destination address to broadcast
m - Set source address to broadcast
s - Shotgun: randomly overwrites a couple of bytes
t - append random bytes (creates broken tagged parameters in beacons/probes)
c - Cut packets short, preferably somewhere in headers or tags
d - Insert random values in Duration and Flags fields
-c [chan,chan,...,chan[:speed]]
Enable channel hopping. When -c h is given, mdk4 will hop an all
14 b/g channels. Channel will be changed every 3 seconds,
if speed is not specified. Speed value is in milliseconds!
-p <pps>
Set speed in packets per second (Default: 250)
ATTACK MODE x: Poc Testing
Proof-of-concept of WiFi protocol implementation vulnerability,
to test whether the device has wifi vulnerabilities.
It may cause the wifi connection to be disconnected or the target device to crash.
-s <pps>
Set speed in packets per second (Default: unlimited)
-c [chan,chan,...,chan[:speed]]
Enable channel hopping. When -c h is given, mdk4 will hop an all
14 b/g channels. Channel will be changed every 3 seconds,
if speed is not specified. Speed value is in milliseconds!
-v <vendor>
file name in pocs dir, default test all.
-A <AP MAC>
set an AP MAC
-S <Station MAC>
set a station MAC.