You are here
迁移

1、简介
迁移就像数据库的版本控制,允许团队简单轻松的编辑并共享应用的数据库表结构,迁移通常和 Laravel 的结构构建器结对从而可以很容易地构建应用的数据库表结构。 Laravel 的 Schema 门面提供了与数据库系统无关的创建和操纵表的支持,在 Laravel 所支持的所有数据库系统中提供一致的、优雅的、平滑的 API。
2、生成迁移
使用 Artisan 命令 make:migration来创建一个新的迁移:
php artisan make:migration create_users_table新的迁移位于 database/migrations目录下,每个迁移文件名都包含时间戳从而允许 Laravel 判断其顺序。 --table和--create 选项可以用于指定表名以及该迁移是否要创建一个新的数据表。这些选项只需要简单放在上述迁移命令后面并指定表名:
php artisan make:migration add_votes_to_users_table --table=users
php artisan make:migration create_users_table --create=users如果你想要指定生成迁移的自定义输出路径,在执行 make:migration 命令时可以使用--path 选项,提供的路径应该是相对于应用根目录的。
3、迁移结构
迁移类包含了两个方法:up 和 down。up 方法用于新增表,列或者索引到数据库,而 down方法就是 up 方法的反操作,和 up里的操作相反。 在这两个方法中你都要用到 Laravel 的表结构构建器来创建和修改表,想要学习 Schema 构建器的更多有用方法,可以查看其文档。例如,让我们先看看创建 flights 表的简单示例:
<?php
use Illuminate\Database\Schema\Blueprint;
use Illuminate\Database\Migrations\Migration;
class CreateFlightsTable extends Migration{
/**
* 运行迁移
*
* @return void
*/
public function up()
{
Schema::create('flights', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->increments('id');
$table->string('name');
$table->string('airline');
$table->timestamps();
});
}
/**
* 撤销迁移
*
* @return void
*/
public function down()
{
Schema::drop('flights');
}
}4、运行迁移
要运行应用中所有未执行的迁移,可以使用 Artisan 命令的 migrate方法。如果你正在使用Homestead 虚拟机,应该在你的虚拟机中运行如下这条命令:
php artisan migrate如果再运行时遇到”class not found“的错误提示,尝试运行 composer dump-autoload 命令然后重新运行迁移命令。 在生产环境中强制运行迁移 有些迁移操作是毁灭性的,这意味着它们可能造成数据的丢失,为了避免在生产环境数据库中运行这些命令,你将会在运行这些命令之前被提示并确认。想要强制运行这些命令而不被提示,可以使用--force:
php artisan migrate --force4.1 回滚迁移
想要回滚最新的一次迁移”操作“,可以使用 rollback 命令,注意这将会回滚最后一批运行的迁移,可能包含多个迁移文件:
php artisan migrate:rollbackmigrate:reset 命令将会回滚所有的应用迁移:
php artisan migrate:reset4.1.1 在单个命令中回滚/迁移
migrate:refresh 命令将会先回滚所有数据库迁移,然后运行migrate 命令。这个命令可以有效的重建整个数据库:
php artisan migrate:refresh
php artisan migrate:refresh --seed5、编写迁移
5.1 创建表
使用Schema 门面上的 create方法来创建新的数据表。create方法接收两个参数,第一个是表名,第二个是获取用于定义新表的Blueprint对象的闭包:
Schema::create('users', function ($table) {
$table->increments('id');
});当然,创建新表的时候,可以使用表结构构建器中的任意列方法来定义数据表的列。
5.1.1 检查表/列是否存在
你可以轻松地使用 hasTable 和 hasColumn 方法检查表或列是否存在:
if (Schema::hasTable('users')) {
//
}
if (Schema::hasColumn('users', 'email')) {
//
}5.1.2 连接&存储引擎
如果你想要在一个数据库连接上执行表结构操作,该数据库连接并不是默认数据库连接,使用 connection方法:
Schema::connection('foo')->create('users', function ($table) {
$table->increments('id');
});要设置表的存储引擎,在表结构构建器上设置 engine 属性:
Schema::create('users', function ($table) {
$table->engine = 'InnoDB';
$table->increments('id');
});5.2 重命名/删除表
要重命名一个已存在的数据表,使用 rename 方法:
Schema::rename($from, $to);要删除一个已存在的数据表,可以使用 drop 或 dropIfExists 方法:
Schema::drop('users');Schema::dropIfExists('users');5.3 创建列
要更新一个已存在的表,使用 Schema 门面上的 table 方法,和 create 方法一样,table 方法接收两个参数:表名和获取用于添加列到表的 Blueprint 实例的闭包:
Schema::table('users', function ($table) {
$table->string('email');
});5.3.1 可用的列类型
当然,表结构构建器包含一系列你可以用来构建表的列类型:

5.3.2 列修改器
除了上面列出的列类型之外,在添加列的时候还可以使用一些其它列”修改器“,例如,要使列默认为null,可以使用nullable 方法:
Schema::table('users', function ($table) {
$table->string('email')->nullable();
});下面是所有可用的列修改器列表,该列表不包含索引修改器:
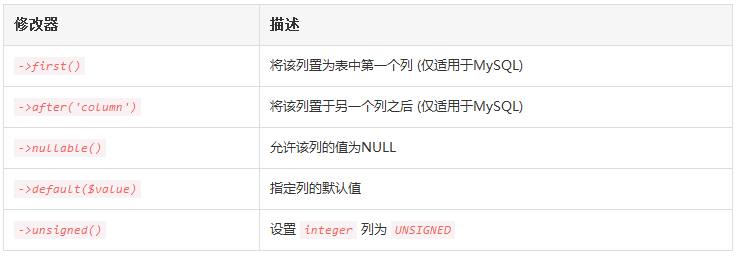
5.4 修改列
5.4.1 先决条件
在修改列之前,确保已经将 doctrine/dbal 依赖添加到 composer.json 文件,Doctrine DBAL 库用于判断列的当前状态并在需要时创建 SQL 查询来对列进行指定的调整。
5.4.2 更新列属性
change 方法允许你修改已存在的列为新的类型,或者修改列的属性。例如,你可能想要增加 string 类型列的尺寸,让我们将 name 列的尺寸从25增加到50:
Schema::table('users', function ($table) {
$table->string('name', 50)->change();
});我们还可以修改该列允许 NULL 值:
Schema::table('users', function ($table) {
$table->string('name', 50)->nullable()->change();
});5.4.3 重命名列
要重命名一个列名,可以使用表结构构建器上的 renameColumn 方法,在重命名一个列之前,确保doctrine/dbal 依赖已经添加到composer.json 文件:
Schema::table('users', function ($table) {
$table->renameColumn('from', 'to');
});注意:enum 类型的列的重命名暂不支持。
5.5 删除列
要删除一个列,使用表结构构建器上的 dropColumn 方法:
Schema::table('users', function ($table) {
$table->dropColumn('votes');
});你可以传递列名数组到dropColumn 方法从表中删除多个列:
Schema::table('users', function ($table) {
$table->dropColumn(['votes', 'avatar', 'location']);
});注意:在从 SQLite 数据库删除列之前,需要添加 doctrine/dbal 依赖到 composer.json文件并在终端中运行composer update 命令来安装该库。
5.6 创建索引
表结构构建器支持多种类型的索引,首先,让我们看一个指定列值为唯一索引的例子。要创建索引,可以使用 unique 方法:
$table->string('email')->unique();此外,你可以在定义列之后创建索引,例如:
$table->unique('email');你甚至可以传递列名数组到索引方法来创建混合索引:
$table->index(['account_id', 'created_at']);5.6.1 可用索引类型
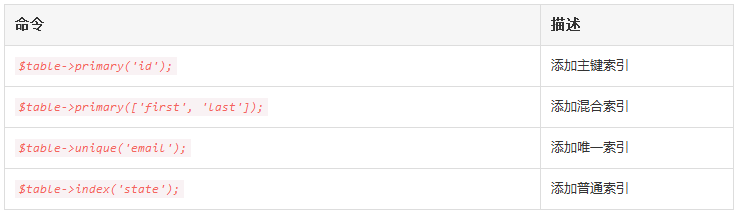
5.7 删除索引
要删除索引,必须指定索引名。默认情况下,Laravel 自动分配适当的名称给索引——简单连接表名、列名和索引类型。下面是一些例子:

5.8 外键约束
Laravel 还提供了创建外键约束的支持,用于在数据库层面强制引用完整性。例如,我们在 posts表中定义了一个引用users表的id列的user_id列:
Schema::table('posts', function ($table) {
$table->integer('user_id')->unsigned();
$table->foreign('user_id')->references('id')->on('users');
});你还可以为约束的“on delete”和“on update”属性指定期望的动作:
$table->foreign('user_id')
->references('id')->on('users')
->onDelete('cascade');要删除一个外键(删除外键),可以使用 dropForeign 方法。外键约束和索引使用同样的命名规则——连接表名、外键名然后加上”_foreign”后缀:
$table->dropForeign('posts_user_id_foreign');